Automatic
Screen
- 1⚓
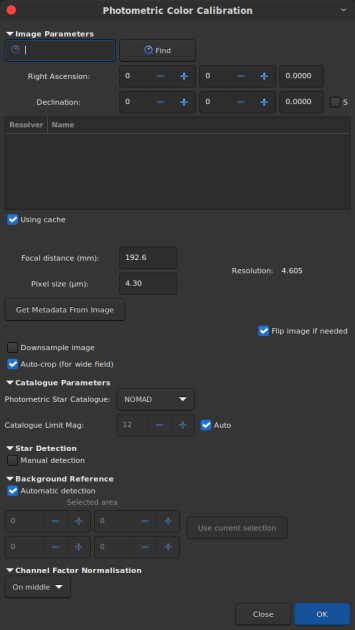
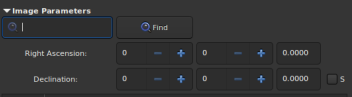
Image Parameters⚓
Enter the identifier or the name of the object which can be seen in the image, either in the center or in the selected area.
- 2⚓
Search field⚓
Several resolvers can be found and displayed in this list. However, it just about getting the coordinates of the center of the object. Choosing one item or the others should not influence the plate-solving or the photometry data, which is based on the selected catalogue.
- 3⚓
Focal distance⚓
Effective focal length of the optical system in millimeter. The value will be updated after plate-solving to display the computed focal length.
Tip
Even if the input value has not to be very accurate, try to give a value with an error not exceeding 20%.
- 4⚓
Pixel size⚓
Pixel size in micrometer.
Note
The image is assumed to have square pixels.
- 5⚓
Resolution⚓
The resolution of the image in arcsec per pixel, automatically determined from the focal and pixel size value.
- 6⚓
Metadata⚓
Click on this button to get focal and pixel size value from the header of the file if they exist (FITS only).
- 7⚓
- 8⚓
Auro-crop⚓
Only use the center of the image (or selection) if the field is too wide.
- 9⚓
Flip image if needed⚓
Flip image at the end of the platesolving if the image is mirrored top-bottom.
- 10⚓
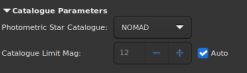
Catalogue Parameters⚓
Choose the online catalogue against one want to compare the image and compute photometry.
- NOMAD is a simple merge of data from the Hipparcos, Tycho-2, UCAC2, Yellow-Blue 6, and USNO-B catalogs for astrometry and optical photometry, supplemented by 2MASS near-infrared. The almost 100 GB dataset contains astrometric and photometric data for about 1.1 billion stars.
- APASS, the AAVSO Photometric All Sky Survey, is performing an all-sky photometric survey. This survey is conducted in eight filters: Johnson B and V, plus Sloan u', g′, r′, i′, z_s and Z. It is valid from about 7th magnitude to about 17th magnitude for over 37 million stars.
You can set the limit the catalogue's star magnitudes by unticking the 'Auto' option.
- 11⚓
AdviceStar Detection⚓
Check this box if you want to select he stars used for plate-solving manually or with the star selection tool (in the PSF window).
Enabling this option disables the Auto-crop feature and user selection.
- 12⚓
Background Reference⚓
Uncheck this box if you want to select the background reference by yourself. It could be useful when nebulae almost cover the whole image.
- 13⚓
Channel Factor Normalization⚓
Select the reference channels against which the two other will have their background value aligned.
- 14⚓
Using cache⚓
The plate-solving relies heavily on Web database queries for the star field. Using a cache will save the queries results for a field center and a field angular size (field of view), to avoid querying several times the same content. This is faster and puts less pressure on the Web service.
The automatic color calibration finds known stars in the image and makes them look like their known color. To do this, Siril must know which part of the sky is seen in the image, so a plate-solving (also called astrometric solution) is required. Then, for each of the main stars of the image, color information (the red, green and blue relative magnitudes) must be acquired. For these two functions, an Internet connection is required, as an online database is queried.
Then, factors are computed for each stars and the average is applied to make red and blue channels match the level of the green channel.
Since star magnitudes are used for plate-solving, the image must be in linear mode.
The photometric color correction window includes the plate-solving step, which can also be done alone. The two tools look very similar. See the documentation on plate-solving.