Updating to match new version of source page |
Updating to match new version of source page |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
Los astrónomos profesionales generalmente usan imágenes con profundidad de 32-bits, pero Siril usa únicamente imágenes de 16-bits (excepto temporalmente para el apilado). Se pueden cargar imágenes de 32-bits pero serán degradadas al ser convertidas a 16-bits. Aún así puede ser útil si la intención es producir imágenes para el público general. | Los astrónomos profesionales generalmente usan imágenes con profundidad de 32-bits, pero Siril usa únicamente imágenes de 16-bits (excepto temporalmente para el apilado). Se pueden cargar imágenes de 32-bits pero serán degradadas al ser convertidas a 16-bits. Aún así puede ser útil si la intención es producir imágenes para el público general. | ||
And more generally, people who want to use free software on free operating systems to process images. Siril can even be used to extract previewed frames from many videos formats. For an overview, see some image processing [[Siril:Results|results]]. | |||
==News== | ==News== | ||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
==Start using Siril / Documentation== | ==Start using Siril / Documentation== | ||
Siril's works internally with [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/FITS FITS] images, unsigned 16-bit per pixel and per channel. All images you want to process with Siril have to be converted using the | Siril's works internally with [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/FITS FITS] images, unsigned 16-bit per pixel and per channel. All images you want to process with Siril have to be converted using the Conversion tab, except for [[SER]] and film sequences which are converted on-the-fly. | ||
Para el pre-procesamiento, Siril usa imagenes ''master'' de offset/bias, darks y flats. Estas imagenes master deben ser procesadas antes de procesar la secuencia de imagenes. Siril actualmente no soporta procesar multiples secuencias al mismo tiempo, por lo que cada capa de la imagen final debe ser procesada de manera independiente antes de ensamblarla en una imagen RGB. | Para el pre-procesamiento, Siril usa imagenes ''master'' de offset/bias, darks y flats. Estas imagenes master deben ser procesadas antes de procesar la secuencia de imagenes. Siril actualmente no soporta procesar multiples secuencias al mismo tiempo, por lo que cada capa de la imagen final debe ser procesada de manera independiente antes de ensamblarla en una imagen RGB. | ||
'''A new [//{{SERVERNAME}}/siril_doc-en/ Web-based documentation]''' or '''[//{{SERVERNAME}}/download/siril-doc-0.9.5-en.pdf PDF format]''' for offline viewing, contain illustrated instructions on how to use particular features of Siril, along with a few videos to illustrate or describe these capabilities. | |||
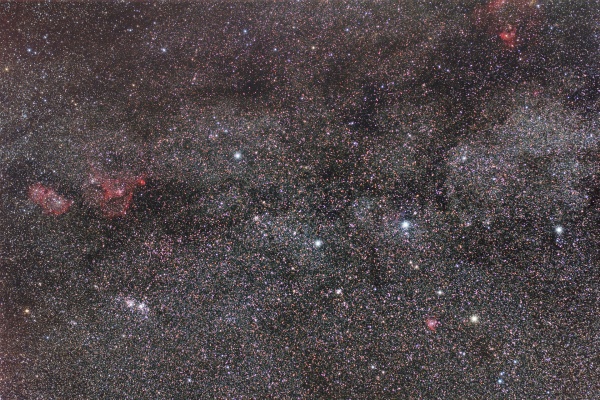
[[File:Siril_stacking_result.png|600px]] | [[File:Siril_stacking_result.png|600px]] | ||
Revision as of 20:30, 10 December 2016
Siril, un software de procesamiento de imágenes gratuito
Siril significa Iris for Linux (sirI-L). Es una herramienta para procesar imágenes astronómicas, capaz de convertir y pre-procesar imágenes, ayudar a alinearlas de modo automático o manual, apilarlas y mejorar las imágenes finales. Esta página es la página para la nueva version de Siril.
Current version is 0.9.5 (stable). See the list of previous versions.

Who should use Siril?
Siril is targeted to amateur astronomers having acquired images and wanting to process them in a semi-automatic way. It provides a more user-friendly interface than Iris' command line as well as more modern and powerful processing algorithms, but it is not yet as automated as DeepSkyStacker or Registax. It also provides a basic command line to access various processing functions.
Siril is now fully capable to pre-process and process deep sky images. One feature still missing for planetary images processing is image deformation, but it is still capable of registering and processing them in an elegant way. The new star detection registration is perfect for deep sky images, but there are also two automatic translation-only registrations, one more suited for planetary and bright nebula images, based on DFT, and another more simple targetted at deep-sky images, based on PSF on a single reference star. Additionally, a manual alignment capability makes it also well fitted for amateur astronomers having feature-less or bad quality images that automatic tools fail to align properly.
Los astrónomos profesionales generalmente usan imágenes con profundidad de 32-bits, pero Siril usa únicamente imágenes de 16-bits (excepto temporalmente para el apilado). Se pueden cargar imágenes de 32-bits pero serán degradadas al ser convertidas a 16-bits. Aún así puede ser útil si la intención es producir imágenes para el público general.
And more generally, people who want to use free software on free operating systems to process images. Siril can even be used to extract previewed frames from many videos formats. For an overview, see some image processing results.
News
For latest updates, see our bug and feature tracking system.
We are looking for volunteer translators, for the software and for the documentation. No programming experience is required. See the translation instructions page for software translation. In any case, check the status of your language translation with cyril (at free-astro.org) if you want to help.
The software is now considered stable. If you find bugs and want to report them (please, do!), contact the team using the links at the bottom of this page, or feel free to report them on the bug report page.
- October 8, 2016
- October 28, 2015
- First stable version available: 0.9.0. Stability updates and minor improvements will occur in the dedicated 0.9 branch.
- June 10, 2015
- New registration method available! It is now possible to register images with an automatic global star detection tool. The algorithm takes into account the translation and the rotation.
- April 13, 2015
- We have been working hard on accelerating stacking algorithms on multi-core CPUs, giving SER a better support and we are also working on the two main lacks of Siril: taking into account rotation and multi-point in registration, for better deep-sky and planetary registrations. These works are in progress, and will take some weeks to complete.
Many improvements have been done over the previous unmaintained version. The command line has been reactivated in large proportions, see the list of currently available commands on the dedicated Commands page. New commands and features have been and are being developed. For a complete list of features, see the 0.9.4 page, the roadmap, or the list of features below.
The roadmap for Siril is being updated for its after-release life. Ideas are stored in the Roadmap page, and the list of known bugs is maintained in the bug tracking page file. The complete changelog is available in the SVN log, a summary is available in the news section above and in the page of each release, as well as in the ChangeLog file. If you want to contribute, you are welcome!
Start using Siril / Documentation
Siril's works internally with FITS images, unsigned 16-bit per pixel and per channel. All images you want to process with Siril have to be converted using the Conversion tab, except for SER and film sequences which are converted on-the-fly.
Para el pre-procesamiento, Siril usa imagenes master de offset/bias, darks y flats. Estas imagenes master deben ser procesadas antes de procesar la secuencia de imagenes. Siril actualmente no soporta procesar multiples secuencias al mismo tiempo, por lo que cada capa de la imagen final debe ser procesada de manera independiente antes de ensamblarla en una imagen RGB.
A new Web-based documentation or PDF format for offline viewing, contain illustrated instructions on how to use particular features of Siril, along with a few videos to illustrate or describe these capabilities.
Lista de Caracateristicas de Siril
New features are being introduced quite regularly. Here is a list of main features:
- Native image format support
- Unsigned 16-bit FITS files (other FITS are converted to this format on-the-fly)
- SER files
- AVI and many other film files, their support is being dropped in favour of SER.
- Image conversion (to the native FITS format only)
- Supported input types: 8-bit and 16-bit BMP, TIFF, JPEG, PNG files, NetPBM binary images, RAW DSLR images.
- Pre-processing of images with multi-channel offset, dark and flat images
- Image registration; supported methods:
- Global star alignment (rotation + translation)
- Translation using DFT centered on an object, generally used for planetary images
- Translation using PSF of a star, generally used for deek-sky images
- Manual translation with two preview renderings of the current image with reference frame in transparency
- Registered sequence export
- Supported export file formats: Siril FITS sequence, SER sequence, uncompressed AVI files, GIF up to 0.9.4, MP4 and WEBM web publising video formats since 0.9.5
- Optionnal cropping and resizing of the exported images
- Image stacking
- Summing
- Median
- Percentile clipping
- Sigma clipping
- Median sigma clipping
- Winsorized sigma clipping
- Linear fit clipping
- Pixel minimum/maximum
- Enhancement and processing of final images
- Lightness/contrast cursors on each layer, different scaling modes (linear, log, square root, squared, asinh, histogram equalisation), negative and false colour rendering and clipping
- Background removal tool
- Cosmetic correction tool
- A command line for various processing functions, only available from the GUI, see the list of available commands.
- A star finding algorithm with PSF information
- Image compositing tool, combining and aligning multiple layers (1 to 6) with custom colours into a resulting image, with luminance layer support
Compilado e Instalacion
See Siril installation page. It documents which binary packages you can get and how to build from source if needed, for multiple operating systems. Siril is a free software, licence is GPL3. It will most likely never run or be supported on Windows family operating systems.
Quien esta detras de Siril?
Vincent is a computer scientist (PhD) and uses Siril as an amateur to process images from a Canon EOS, a QSI and a Basler camera on a 410mm telescope.
Cyril is a physicist (PhD), now IT engineer at CNRS, motivating new developments and providing high quality processing algorithms to Siril.
Laurent is a senior IT project manager and also uses Siril to process images from a Canon EOS and a ZWO camera on a 254mm telescope. He manages the formatting of the documentation, using Scenari technology.
François Meyer escribio las versiones iniciales (hasta la v0.8). Aqui esta el Sourceforge proyecto original y sitio web.
See the AUTHORS file for the complete list of contributors.
If you like the software, please help us by contributing with the Donate button on the top right. Siril took us a lot of time and we still have to pay for the server.