(Created page with "=Tutorial for a complete image processing=") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Tutorial for a complete image processing= | =Tutorial for a complete image processing= | ||
Once you get your pre-processed and stacked image (fore more details see [[Siril:Manual#Tutorial_for_a_complete_sequence_processing|here]]), the process stage can start. | |||
This tutorial will present to you which different processes you can use, however there are no absolute rules. Feel free to try many processus by adjusting parameters. We will use the image used in the preprocessing step, M8-M20. | |||
==Background extraction== | |||
By selecting "Histogram Equalization" as display view, you can quickly check that image contains sky gradient due to light pollution, or in this case, Moon light. | |||
[[File:Siril inal_result.png|700px]] | |||
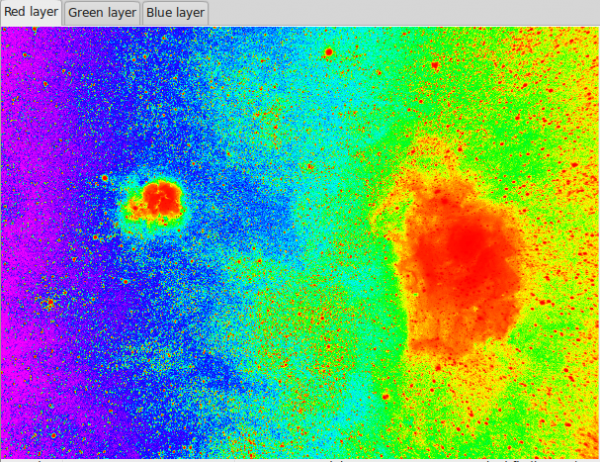
The rainbow colormap can also help you to see the gradient: | |||
[[File:Siril_gradient_rainbow.png|600px]] | |||
So, before applying any filter or processes, the first step consists to remove this sky gradient. To do that, Siril provides a [[Siril:Manual#Background_extraction|background extraction tool]], but your image must be cropped before in order to remove any frame that could misleading the tool. | |||
In this case I use the 2D-Surface spline interpolation and it is very important to make several test by adjusting interatively the parameters. Once you have a background model with no signal from nebula (use the display mode to check everything), you can apply the correction. | |||
[[File:Siril_gradient_2D-S_spline.png|600px]] | |||
Two types of corrections have been implemented in Siril: | |||
* Subtraction | |||
* Division | |||
Additive phenomena like light pollution gradients should be corrected by subtraction but multiplicative effects like vignetting should be fixed by a division. But in the last case, the correct procedure is to correct the image with flat field during pre-processing step. | |||
Revision as of 12:19, 22 October 2014
Tutorial for a complete image processing
Once you get your pre-processed and stacked image (fore more details see here), the process stage can start.
This tutorial will present to you which different processes you can use, however there are no absolute rules. Feel free to try many processus by adjusting parameters. We will use the image used in the preprocessing step, M8-M20.
Background extraction
By selecting "Histogram Equalization" as display view, you can quickly check that image contains sky gradient due to light pollution, or in this case, Moon light.
The rainbow colormap can also help you to see the gradient:
So, before applying any filter or processes, the first step consists to remove this sky gradient. To do that, Siril provides a background extraction tool, but your image must be cropped before in order to remove any frame that could misleading the tool.
In this case I use the 2D-Surface spline interpolation and it is very important to make several test by adjusting interatively the parameters. Once you have a background model with no signal from nebula (use the display mode to check everything), you can apply the correction.
Two types of corrections have been implemented in Siril:
- Subtraction
- Division
Additive phenomena like light pollution gradients should be corrected by subtraction but multiplicative effects like vignetting should be fixed by a division. But in the last case, the correct procedure is to correct the image with flat field during pre-processing step.