Marked this version for translation |
|||
| (14 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<languages /> | |||
<translate> | |||
<!--T:11--> | |||
<span style="color: #ff0090; font-weight: bold; text-align: center; margin: 2em; font-size: 125%;">This page is the old documentation for early versions of Siril 0.9. Please refer to the new documentation on [https://siril.readthedocs.io/en/stable/ siril.readthedocs.io] or the new tutorials on [https://siril.org/tutorials siril.org] instead.</span> | |||
=Siril processing tutorial= <!--T:1--> | |||
<!--T:2--> | |||
* → '''Convert your images in the FITS format Siril uses (image import)''' | * → '''Convert your images in the FITS format Siril uses (image import)''' | ||
* [[Siril:Tutorial_sequence|Work on a sequence of converted images]] | * [[Siril:Tutorial_sequence|Work on a sequence of converted images]] | ||
* [[Siril:Tutorial_preprocessing|Pre-processing images]] | * [[Siril:Tutorial_preprocessing|Pre-processing images]] | ||
* [[Siril:Tutorial_manual_registration|Registration ( | * [[Siril:Tutorial_manual_registration|Registration (Global star alignment)]] | ||
* [[Siril:Tutorial_stacking|Stacking]] | * [[Siril:Tutorial_stacking|Stacking]] | ||
==Convert your images in the FITS format Siril uses (image import)== | ==Convert your images in the FITS format Siril uses (image import)== <!--T:3--> | ||
To process your images with Siril, you must convert them to the FITS format it uses (16-bit unsigned, bottom-top order, 1 or 3 axes). Fortunately, Siril is able to convert some image formats to this format, | <!--T:4--> | ||
To process your images with Siril, you must convert them to the FITS format it uses (16-bit unsigned, bottom-top order, 1 or 3 axes). Fortunately, Siril is able to convert some image formats to this format, RAW, TIFF, JPEG, PIC (Christian Buil's IRIS image format) PNG, BMP and NetPBM binaries for images, AVI and other films. | |||
First, the working directory has to be set. Images will be | <!--T:5--> | ||
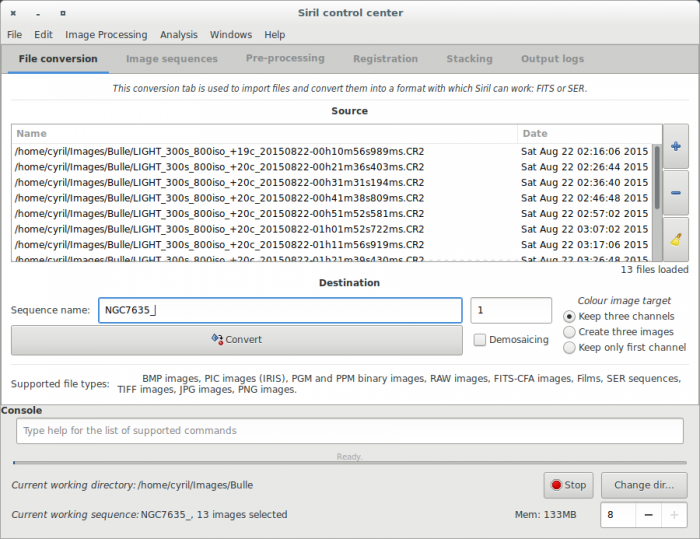
First, the working directory has to be set. Images will be converted to this directory. Click on "Change dir" at bottom right of the window to change it or type [[Siril:Commands#cd|cd]] [your directory] in the console input command. | |||
<!--T:6--> | |||
Click on the "+" button to add the files to be converted. All supported formats can be selected at same time and will be converted in a sequence of files starting with the generic name you've specified just below. Created file names will be in the form <code>Name_XXX</code>, where XXX is the number of each image in the sequence. The button "Demosaicing" must be unchecked int order to convert RAW files into CFA ([https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_filter_array Color Filter Array]) monochrome FITS pictures, a necessary step to pre-process DSLR images. | |||
[[File:Siril_conversion_screen.png]] | <!--T:7--> | ||
[[File:Siril_conversion_screen.png | 700px]] | |||
[[File:Siril_conversion_screen2.png | 700px]] | |||
<!--T:8--> | |||
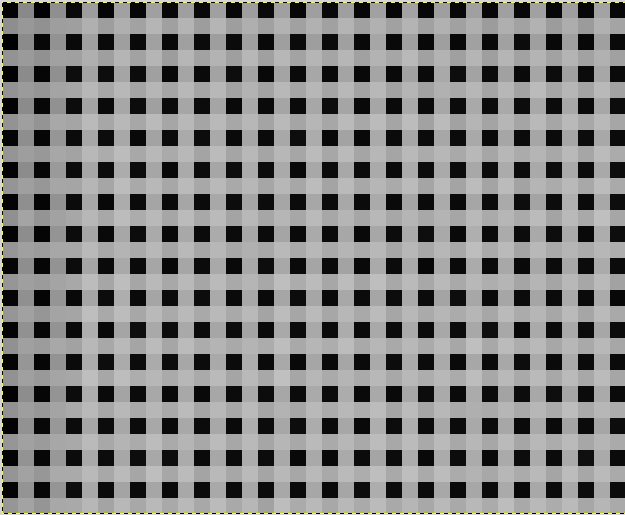
Indeed, due to Bayer matrix consideration, the RGB result of your RAW image is an interpolated picture. In consequence pre-processing interpolated data will give wrong results. Contrary to RGB image, CFA image represent the entire sensor data with the Bayer pattern. The following image shows you a crop of a CFA image. Note that the Bayer pattern (RGGB on this example) is visible. | |||
<!--T:9--> | |||
[[File:Siril_Bayer_Pattern.png]] | |||
<!--T:10--> | |||
Next item of the tutorial: [[Siril:Tutorial_sequence|Work on a sequence of converted images]]. | Next item of the tutorial: [[Siril:Tutorial_sequence|Work on a sequence of converted images]]. | ||
</translate> | |||
Latest revision as of 22:38, 16 September 2023
This page is the old documentation for early versions of Siril 0.9. Please refer to the new documentation on siril.readthedocs.io or the new tutorials on siril.org instead.
Siril processing tutorial
- → Convert your images in the FITS format Siril uses (image import)
- Work on a sequence of converted images
- Pre-processing images
- Registration (Global star alignment)
- Stacking
Convert your images in the FITS format Siril uses (image import)
To process your images with Siril, you must convert them to the FITS format it uses (16-bit unsigned, bottom-top order, 1 or 3 axes). Fortunately, Siril is able to convert some image formats to this format, RAW, TIFF, JPEG, PIC (Christian Buil's IRIS image format) PNG, BMP and NetPBM binaries for images, AVI and other films.
First, the working directory has to be set. Images will be converted to this directory. Click on "Change dir" at bottom right of the window to change it or type cd [your directory] in the console input command.
Click on the "+" button to add the files to be converted. All supported formats can be selected at same time and will be converted in a sequence of files starting with the generic name you've specified just below. Created file names will be in the form Name_XXX, where XXX is the number of each image in the sequence. The button "Demosaicing" must be unchecked int order to convert RAW files into CFA (Color Filter Array) monochrome FITS pictures, a necessary step to pre-process DSLR images.
Indeed, due to Bayer matrix consideration, the RGB result of your RAW image is an interpolated picture. In consequence pre-processing interpolated data will give wrong results. Contrary to RGB image, CFA image represent the entire sensor data with the Bayer pattern. The following image shows you a crop of a CFA image. Note that the Bayer pattern (RGGB on this example) is visible.
Next item of the tutorial: Work on a sequence of converted images.